Package javax.measure.unit
package javax.measure.unit
Provides support for programatic unit handling.
Standart/NonStandard Units
Standard units and prefixes are provided by theSI class (Système International d'Unités) and
about 50 non-standard units are available through the
NonSI class.
Usage examples:
[code] import javax.measure.Scalar; import javax.measure.Measure; import javax.measure.unit.*; import javax.measure.quantity.*; import static javax.measure.unit.SI.*; import static javax.measure.unit.NonSI.*; import static javax.measure.unit.Dimension.*; public class Main { public void main(String[] args) { // Conversion between units. System.out.println(KILO(METRE).getConverterTo(MILE).convert(10)); // Retrieval of the system unit (identifies the measurement type). System.out.println(REVOLUTION.divide(MINUTE).getSystemUnit()); // Dimension checking (allows/disallows conversions) System.out.println(ELECTRON_VOLT.isCompatible(WATT.times(HOUR))); // Retrieval of the unit dimension (depends upon the current model). System.out.println(ELECTRON_VOLT.getDimension()); } } > 6.2137119223733395 > rad/s > true > [L]²·[M]/[T]² [/code]Unit Parameterization
Units are parameterized (<Q extendsQuantity>) to
enforce compile-time checks of units/measures consistency, for example:[code]
UnitUML Diagram
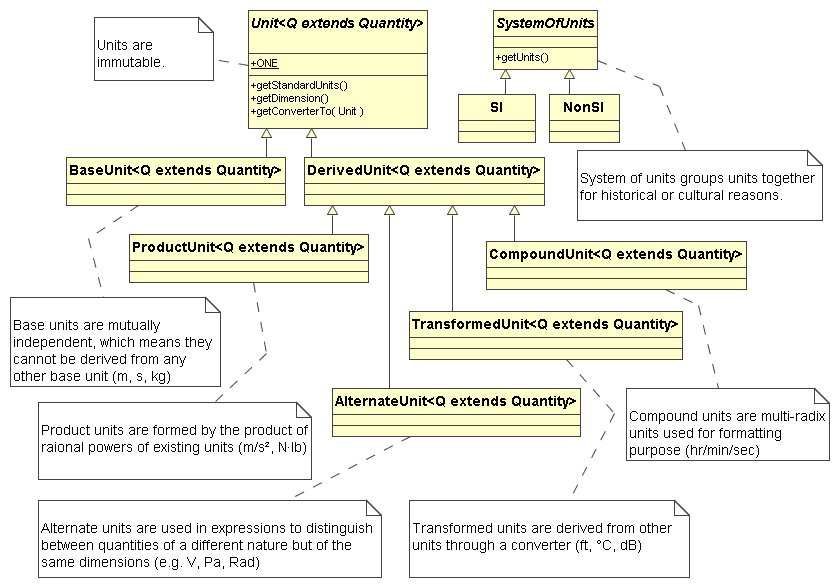
-
ClassDescriptionAlternateUnit<Q extends Quantity>This class represents the units used in expressions to distinguish between quantities of a different nature but of the same dimensions.This class represents the building blocks on top of which all others units are created.CompoundUnit<Q extends Quantity>This class represents the multi-radix units (such as "hour:min:sec").DerivedUnit<Q extends Quantity>This class identifies the units created by combining or transforming other units.This class represents the dimension of an unit.This interface represents the mapping between
base unitsanddimensions.This class contains units that are not part of the International System of Units, that is, they are outside the SI, but are important and widely used.ProductUnit<Q extends Quantity>This class represents units formed by the product of rational powers of existing units.This class contains SI (Système International d'Unités) base units, and derived units.This class represents a system of units, it groups units together for historical or cultural reasons.TransformedUnit<Q extends Quantity>This class represents the units derived from other units usingconverters.This class represents a determinatequantity(as of length, time, heat, or value) adopted as a standard of measurement.This class provides the interface for formatting and parsingunits.This class represents the ASCIIFormat format.This class represents the standard format.